A-Book vs B-Book Brokers - How do they differ?
When trading in the forex or CFD markets, one of the most critical decisions traders make is choosing the right broker. However, not all brokers operate the same way. There are two broad categories of forex brokers which include A-Book brokers and B-Book Brokers. Understanding the difference between these two types is essential because it affects trade execution, broker profitability, and potential conflicts of interest.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the A-Book vs B-Book broker models to explore their differences, advantages, disadvantages, and how each affects retail traders. Let’s begin by understanding what A-Book brokers are.
Understanding the A-Book Broker Model
An A-Book forex broker is a type of broker that operates using a Straight Through Processing (STP) or Electronic Communications Network (ECN) execution model. In this model, the broker acts as an intermediary and directly passes client orders to their liquidity providers. The liquidity providers then execute the trades on the interbank market.
A Book brokers simply act as conduits, routing traders’ orders directly to the broader interbank market or a pool of liquidity providers. The liquidity providers can include major banks, financial institutions, hedge funds, and other market participants that constantly buy and sell currencies. The broker essentially matches the trader's order with a corresponding order from a liquidity provider, executing the trade at the best available price.
Key Characteristics of A-Book Brokers
- No Conflict of Interest - Since A-Book brokers do not profit directly from their clients' losses, there is inherently less conflict of interest. Their role is only to facilitate trades efficiently, regardless of whether the client makes or loses money.
- Direct Market Access - Traders gain access to the same prices and liquidity available to institutional players. This often results in tighter spreads.
- Variable Spreads - Spreads offered by A-Book brokers are typically variable, meaning they fluctuate based on the prevailing market conditions and the supply and demand for specific currency pairs. During periods of high volatility or low liquidity, spreads may widen.
- Commission-Based Revenue - A-Book brokers usually feature accounts with commission-based revenue structures. While they may also feature spread-only accounts, accounts with commissions are common.
- Transparency - The routing of trades to external liquidity providers fosters a greater degree of transparency in the execution process. Moreover, traders often have access to detailed execution reports.
Benefits of Trading with an A-Book Broker
- Potentially Better Pricing - Access to the interbank market can result in tighter spreads and more favourable execution prices, especially during liquid market conditions.
- Faster Execution - A-Book execution aims for fast order processing with minimal delays.
- Reduced Conflict of Interest - The broker's revenue model is primarily based on transaction fees, theoretically minimising the incentive to trade against their clients.
- Greater Transparency - Traders often have more visibility into how their orders are being executed.
Potential Drawbacks of Trading with an A-Book Broker
- Commissions Can Add Up -While spreads can be low, the commissions charged by some A-Book brokers can be fairly high. As such, frequent traders may incur higher transaction costs.
- Broker Avoids Risk - A-Book brokers pass the market risk to other players in the industry.
Understanding the B-Book Broker Model
A B-Book forex broker is a type of broker that acts as the counterparty to their clients' trades. They do this by operating a dealing desk which allows them to execute trades within their own liquidity pool. Such brokers are willing to buy when the trader wants to sell and willing to sell when the trader wants to buy. This means the broker effectively takes the opposite side of a client's trade.
The primary way B-Book brokers profit is when their clients lose trades. If a client buys EUR/USD and then sells it at a lower price, the client's loss becomes the broker's profit. They also profit from the spread. Here are some key characteristics of B-Book brokers.
Key Characteristics of B-Book Brokers
- Dealing Desk (DD) - B-Book brokers have a dealing desk that can intervene in trade execution, although this is less common with automated systems. All trades are filled internally, not passed to external liquidity providers.
- Potential Conflict of Interest - A significant point is the inherent conflict of interest. The broker profits when traders lose, which can raise concerns about fair practices.
- Internalising Trades - Many of the client's trades are matched internally within the broker's system without ever reaching the external market.
- Instant Execution - They can often provide instant order execution as they are filling the orders internally and don't have to rely on external market conditions.
- Fixed or Variable Spreads - Spreads can be fixed or variable, depending on how the broker sets them. However, they are usually wider than A-Book brokers.
Benefits of Trading with a B-Book Broker
- Fixed Spreads - Many B-Book brokers offer fixed spreads, which can be attractive to traders who prefer predictable costs.
- Faster Execution - Internal execution can sometimes lead to quicker order fills, especially in volatile markets.
- Consistency - Market makers are able to control their own pricing, which allows them to keep spreads consistent, providing more predictable trading costs.
Potential Drawbacks of Trading with a B-Book Broker
- Conflict of Interest - Since the broker profits from client losses, there can be a potential conflict of interest.
- Requotes - In volatile market conditions, market makers may issue requotes, where the requested price is no longer available.
Key Differences Between A-Book Brokers and B-Book Brokers
| Feature | A-Book Broker | B-Book Broker |
| Execution Model | Straight Through Processing (STP) or Electronic Communication Network (ECN) | Acts as a Market Maker (Dealing Desk) |
| Order Routing | Orders are passed directly to liquidity providers (interbank market, other brokers). | Orders are typically kept in-house and executed against the broker. |
| Conflict of Interest | Minimal, the broker profits strictly from trading fees. | Higher, the broker profits from client losses (acting as counterparty). |
| Spreads | Variable, often tighter, reflecting market conditions. | Can be fixed or variable, potentially wider as the broker marks them up. |
| Transparency | Higher, as trades are executed in the broader market. | Lower, as the broker controls the execution within their system. |
| Execution Speed | Generally fast, dependent on liquidity providers. | Can be very fast, as execution is internal. May involve requotes. |
| Liquidity Access | Provides access to deeper liquidity pools. | Limited to the broker's own capital and risk management. |
Now that we understand the fundamental characteristics, differences, and pros and cons of each broker model, let’s examine a few top brokers representing both execution types.
Some Top A-Book Brokers
Pepperstone
Pepperstone is widely regarded as one of the top A-Book brokers globally, operating under an ECN model. This broker does not maintain a proprietary trading desk. Instead, it sources pricing from a broad network of external liquidity providers. This includes leading global banks and financial institutions. This approach grants traders access to deep liquidity, which contributes to consistently tight spreads and fast trade execution.
The broker offers two main types of trading accounts, which are the Standard Account and the Razor Account. The Standard Account offers spreads starting from 1.0 pips with no additional commission fees. In contrast, the Razor Account features raw spreads from as low as 0.0 pips and applies a commission per trade based on the trading platform a trader uses.
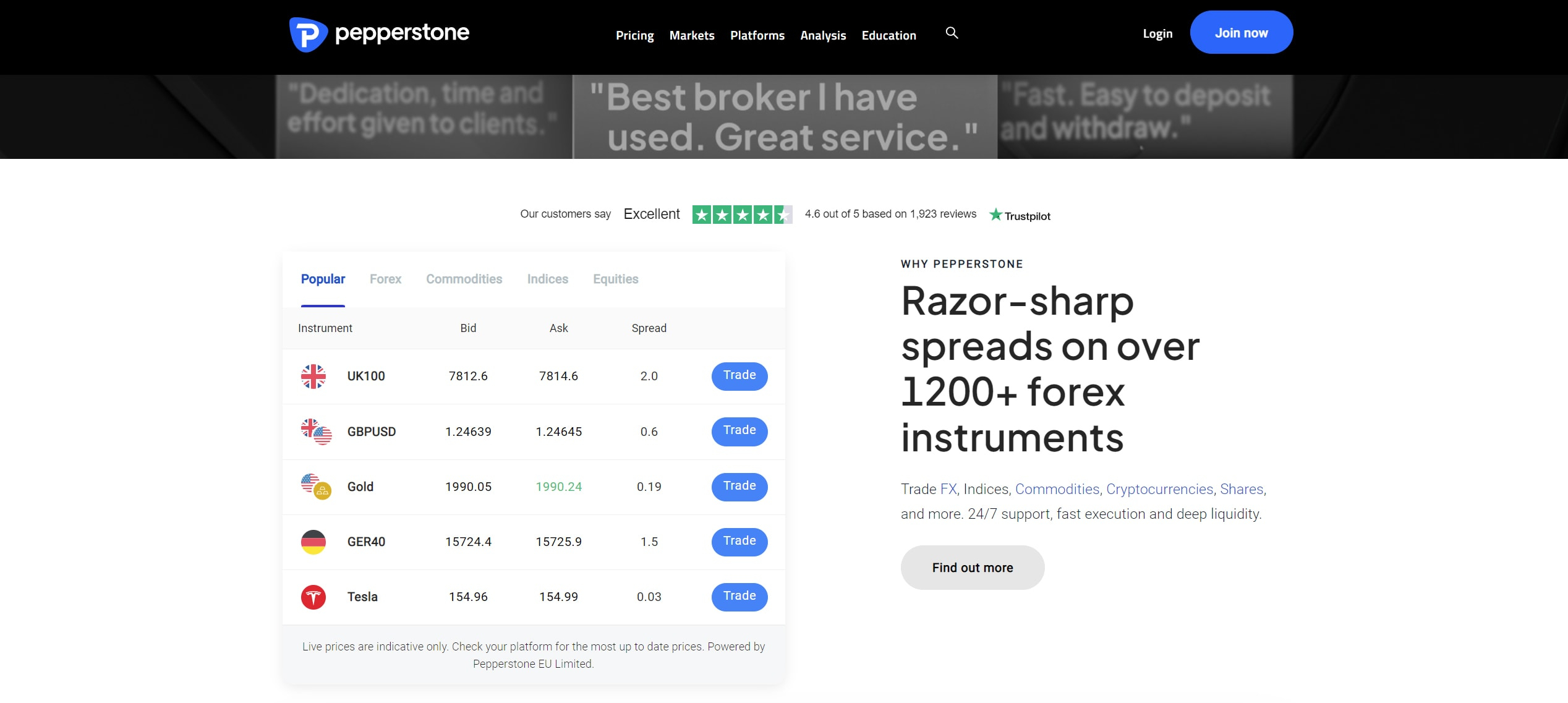
Traders using MetaTrader 4 or MetaTrader 5 pay $3.50, €2.60, £2.25, or CHF 3.30 per side per standard lot, depending on the base currency of their account. Pepperstone Trading Platform and TradingView users pay a commission of $3.5 per side per lot. cTrader offers a slightly lower commission of $3.00 per side per lot. For accounts in currencies other than USD on TradingView, cTrader, and the Pepperstone Trading Platform, commissions are converted using the spot exchange rate.
Pepperstone's robust regulatory standing further solidifies its reputation. The broker holds licenses from several respected financial regulators worldwide. These include the FCA in the UK, the ASIC in Australia, the CySEC in Cyprus, the BaFin in Germany, and the CMA right here in Kenya.
75.3% of retail CFD accounts lose money
FP Markets
FP Markets is another top-rated A-Book broker that utilises an ECN execution model, meaning it does not have a dealing desk. This broker streams pricing directly from its liquidity providers to traders using an Electronic Communication Network. FP Markets aggregates liquidity from top-tier, regulated financial institutions, providing deep liquidity pools and competitive pricing. Coupled with low-latency technology, this setup delivers some of the fastest order execution speeds in the industry.
Traders with FP Markets can choose between two primary account types: the Standard Account and the Raw Account. The Standard Account features spreads starting from 1.0 pips on major forex pairs, with no commission charges. In contrast, the Raw Account offers raw spreads from as low as 0.0 pips, along with a commission of $3 per side per standard lot traded.
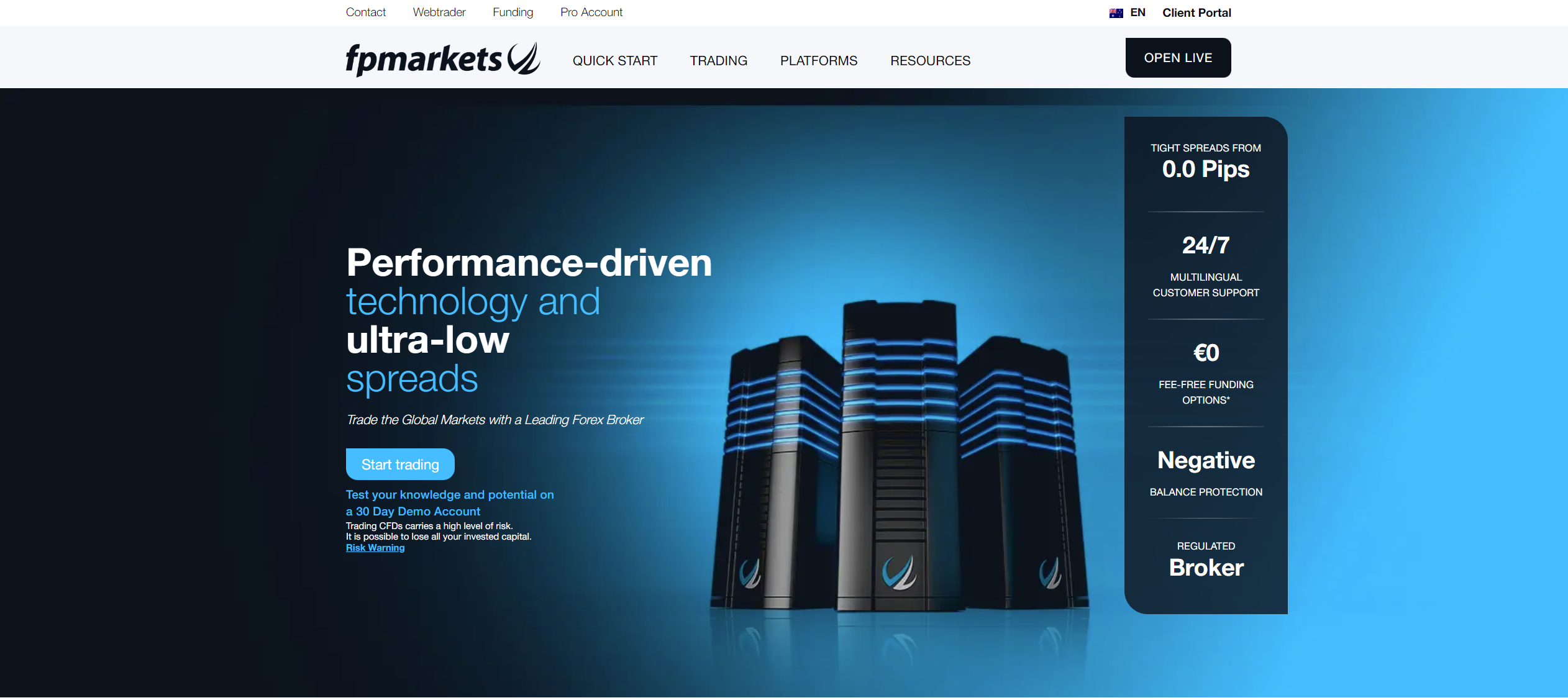
Beyond competitive pricing and execution, FP Markets stands out for the wide range of instruments it offers. Traders have access to over 10,000 tradable products. These include CFDs on forex, indices, commodities, metals, stocks, bonds, and ETFs. To trade these diverse markets, clients can utilise a range of popular platforms, such as MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, cTrader, and TradingView.
Regulation is another strong point for FP Markets. The broker is licensed and overseen by several well-respected financial regulators, including the ASIC in Australia, the CySEC in Cyprus, the FSCA in South Africa, and the CMA in Kenya, among others.
72.44% of retail CFD accounts lose money
Some Top B-Book Brokers
XM
XM is a well-known market maker broker that operates with its own dealing desk. This means that the broker sets its own bid and ask prices for the various trading instruments it offers. XM provides access to over 1,000 trading instruments, which include CFDs on forex, equity indices, stocks, shares, cryptocurrencies, commodities, metals, and energies. Traders can access these markets through various platforms provided by XM, such as MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and the broker’s proprietary mobile trading app.
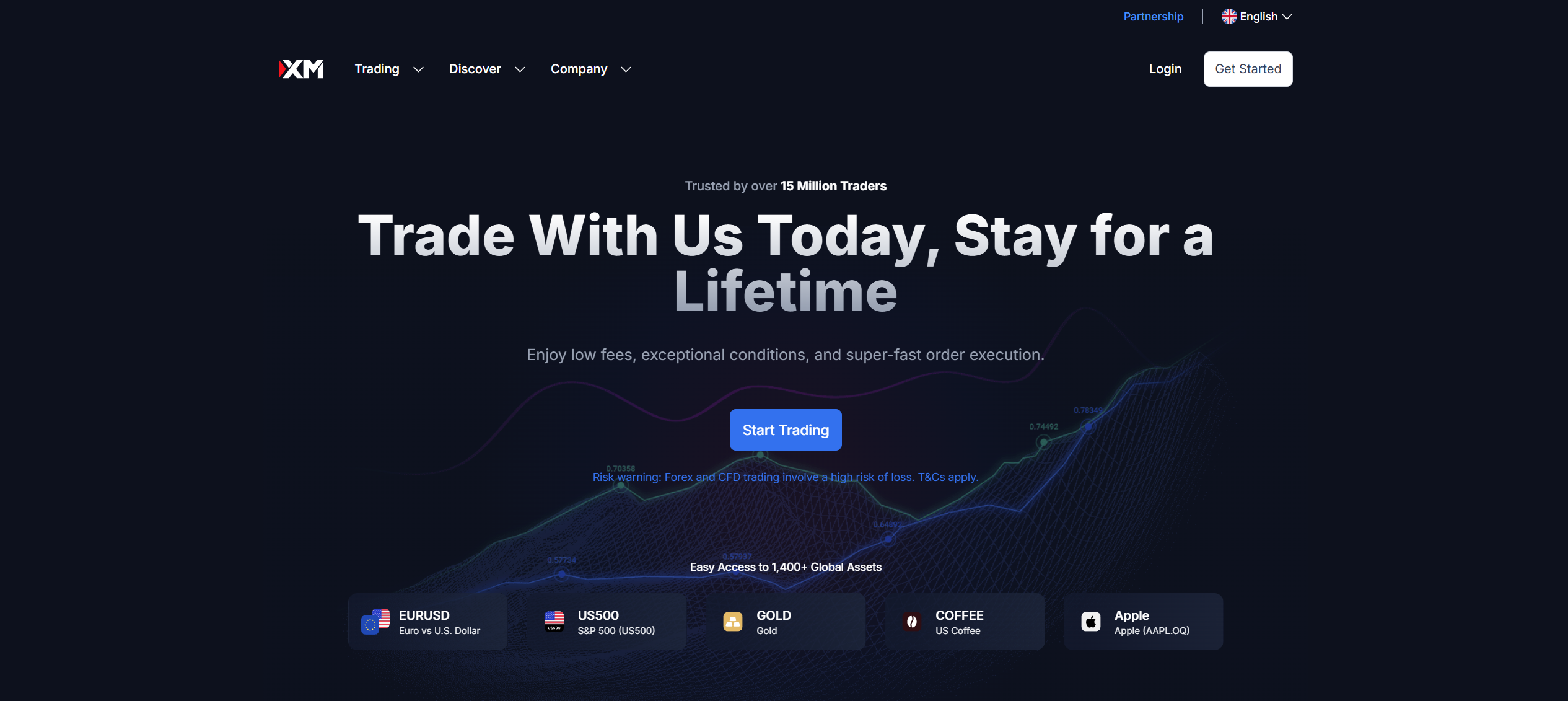
XM provides competitively low spreads across three main account types. The Standard Account features spreads starting from 1.6 pips on major forex pairs, with no commission fees. For traders seeking even tighter spreads, the XM Ultra Low Account offers spreads from as low as 0.8 pips, also commission-free. The broker also offers a Shares Account, which applies commissions based on the specific share being traded and the trade size.
In terms of oversight, XM maintains strong regulatory compliance. This broker operates under the supervision of the CySEC, the ASIC, the DFSA in Dubai, and the FSC in Belize.
75.18% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider.
XTB
XTB has established itself as a leading B-Book broker. As a market maker, XTB provides liquidity to its clients by quoting its own bid and ask prices. The broker offers a diverse selection of financial instruments. These include CFDs on forex, commodities, cryptocurrencies, indices, stocks, and ETFs. In addition to CFDs, XTB also provides access to real stocks and ETFs, allowing traders to invest in actual underlying assets.
A key feature of XTB is its award-winning proprietary platform, xStation 5, which is popular for its user-friendly interface. XTB generally offers competitive spreads, which can vary depending on market conditions. It features tight spreads starting from 0.5 pips on major currency pairs, with no commission fees.
Furthermore, XTB operates as a regulated broker with licenses from several reputable financial authorities. This broker has regulations by the CySEC, the FCA, the KNF in Poland, and the FSC in Belize.
75-78% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider.
Final Verdict
Understanding the fundamental differences between A-Book and B-Book forex brokers is crucial for traders. While both models facilitate trading, their mechanisms, revenue models, and potential conflicts of interest differ significantly.
The choice between an A-Book and a B-Book broker ultimately depends on a trader's individual needs, trading style, and risk tolerance. Traders prioritising transparency, tight spreads, and direct market access may find A-Book brokers more suitable. In contrast, traders seeking fixed spreads and instant execution may be drawn to B-Book brokers.
Whether you choose an A-Book or B-Book broker, always do your due diligence. Read the broker's terms, test execution on a demo account, and verify their regulatory status. And remember, success in trading comes from strategy, discipline, and risk management, not from the broker’s execution model alone.
Top-Tier Trusted Brokers
The table below contains links to 3rd party websites of our top partners from whom we receive compensation at no additional cost to you.